Target: Nipah virus
Nipah virus is a deadly, bat-borne zoonotic virus. It has a high mortality rate (up to 75%) and was first found in Southeast Asia in 1998. Once infected, individuals experience a wide variety of symptoms ranging from fever and headaches to encephalitis and severe respiratory distress.
Glycoprotein G (gpG) on the surface of the virus binds to human ephrin B2 and B3 receptors on human cells, particularly in the nervous system.
Today, there are a few anti-gpG monoclonal antibodies that are making their way through human trials: m102.4, MBP1F5, and mAb92, but there’s still a need for developing more therapeutics against Nipah virus. We participated in the Adaptyv Bio Nipah Binder Competition, submitting ~160 scFv candidates using our 🦋peleke-1 antibody language models.
So, how’d we do?
One of our best candidates, sbio-nipahgpg-120 (in yellow), bound to glycoprotein G (in grey).
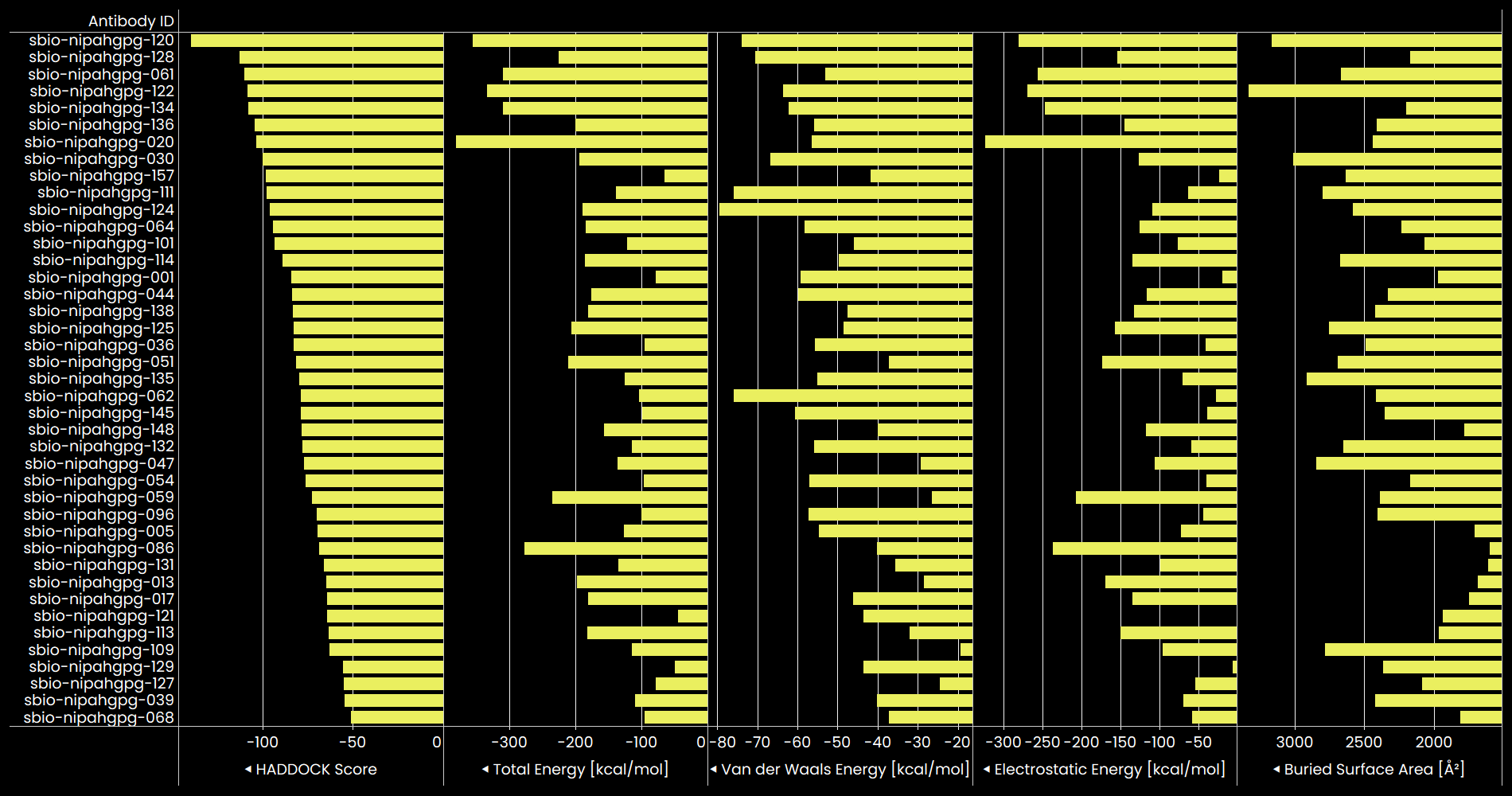
Various binding affinity metrics of our generated anti-gpG antibody candidates.
Top 10 Candidates (by lowest HADDOCK score and iPDE < 10)